How do I find SQL Server version?
Method 1: SQL Server Management Studio
Method 2: Windows Explorer – file properties
Method 3: Windows Registry editor
Method 4: SQL Server ERRORLOG file
GUI tools
Method 1: Using SQL Server Management Studio
The SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is the integrated environment for managing your SQL Server infrastructure. Management Studio is now a completely standalone product, not tied to any specific version or edition of SQL Server, and no longer requires licensing of any kind.
Option A: Object Explorer:
Connect to the server by using Object Explorer in SQL Server Management Studio. When Object Explorer is connected, it shows version information in parentheses.
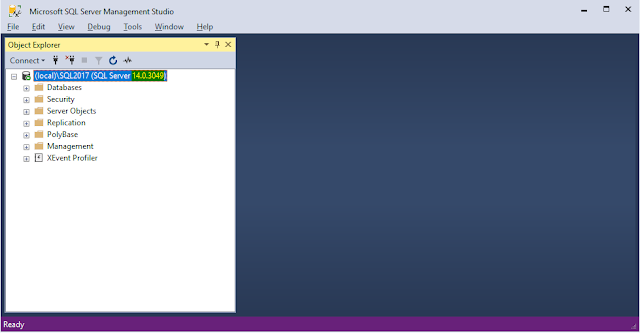
Option B: Server Properties dialog:
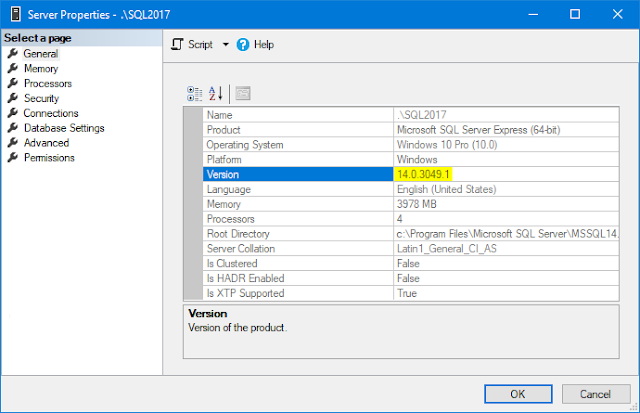
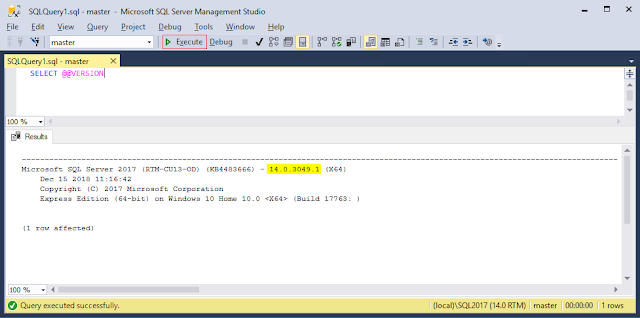
Option C: Execute SQL statement:
Method 2: Windows Explorer – file properties
Example:
Path: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.SQL2017\MSSQL\Binn
File: sqlservr.exe
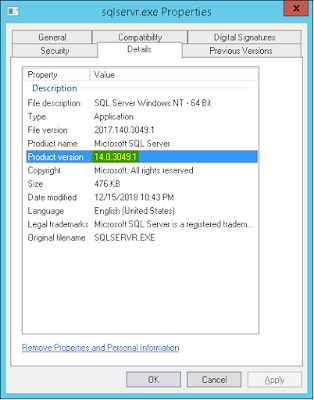
Method 3: Windows Registry editor
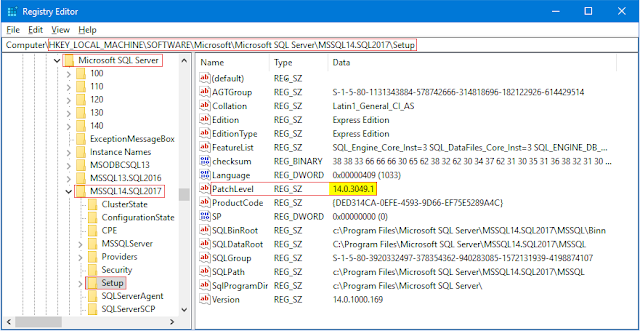
Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL{MajorVersion}.{InstanceName}\Setup
Value: PatchLevel
Example:
SQL Server 2017 (→ major version "14"), instance name "SQL2017"
Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.SQL2017\Setup
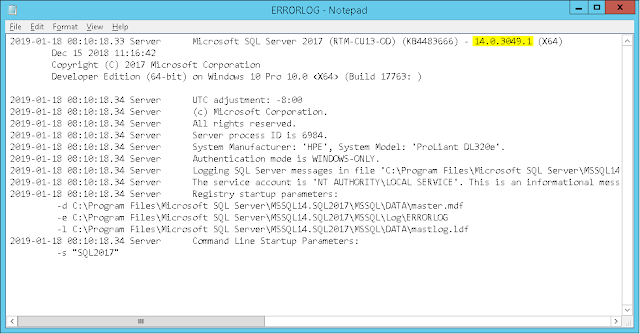
Method 4: SQL Server ERRORLOG file
Path: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL{MajorVersion}.{InstanceName}\MSSQL\Log
File: ERRORLOG (without extension)
Example:
SQL Server 2017 (→ major version "14"), instance name "SQL2017"
Path: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.SQL2017\MSSQL\Log
From command line
Possible SQL statements:
SELECT @@VERSION;
Typical results:
Microsoft SQL Server 2017 (RTM-CU13-OD) (KB4483666) - 14.0.3049.1 (X64)
Dec 15 2018 11:16:42
Copyright (C) 2017 Microsoft Corporation
Developer Edition (64-bit) on Windows 10 Pro 10.0 <X64> (Build 17763: )
(1 row affected)
Microsoft SQL Server 2019 (RTM-GDR) (KB4517790) - 15.0.2070.41 (X64)
Oct 28 2019 19:56:59
Copyright (C) 2019 Microsoft Corporation
Developer Edition (64-bit) on Windows 10 Pro 10.0 <X64> (Build 17763: )
(1 row affected)
-or-
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY('ProductVersion') AS ProductVersion, SERVERPROPERTY('ProductLevel') AS ProductLevel, SERVERPROPERTY('Edition') AS Edition, SERVERPROPERTY('ProductUpdateLevel') AS ProductUpdateLevel, SERVERPROPERTY('ProductUpdateReference') AS ProductUpdateReference;
Typical result:
ProductVersion ProductLevel Edition ProductUpdateLevel ProductUpdateReference
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
14.0.3049.1 RTM Developer Edition (64-bit) CU13 KB4483666
(1 row affected)
-or-
EXEC sys.xp_msver;
Typical result:
Index Name Internal_Value Character_Value
------ -------------------- -------------- ------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 ProductName NULL Microsoft SQL Server
2 ProductVersion 917504 14.0.3049.1
3 Language 1029 English (United States)
4 Platform NULL NT x64
5 Comments NULL SQL
6 CompanyName NULL Microsoft Corporation
7 FileDescription NULL SQL Server Windows NT - 64 Bit
8 FileVersion NULL 2017.0140.3049.01 ((SQLServer2017-CU13-OD).181215-1843)
9 InternalName NULL SQLSERVR
10 LegalCopyright NULL Microsoft. All rights reserved.
11 LegalTrademarks NULL Microsoft SQL Server is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
12 OriginalFilename NULL SQLSERVR.EXE
13 PrivateBuild NULL NULL
14 SpecialBuild 199819265 NULL
15 WindowsVersion 199819265 6.3 (17763)
16 ProcessorCount 4 4
17 ProcessorActiveMask NULL f
18 ProcessorType 8664 NULL
19 PhysicalMemory 3978 3978 (4171210752)
20 Product ID NULL NULL
(20 rows affected)
You can also use specific option:
EXEC sys.xp_msver 'ProductVersion';
Typical result:
Index Name Internal_Value Character_Value
------ -------------------- -------------- ---------------
2 ProductVersion 917504 14.0.3049.1
(1 row affected)
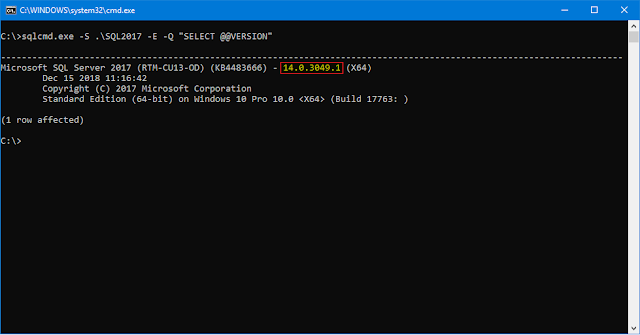
Method 5: SQLCMD Utility
SQLCMD is a part of the SQL Server Client Tools.
sqlcmd.exe -S ServerName\InstanceName -E -Q "SELECT @@VERSION"
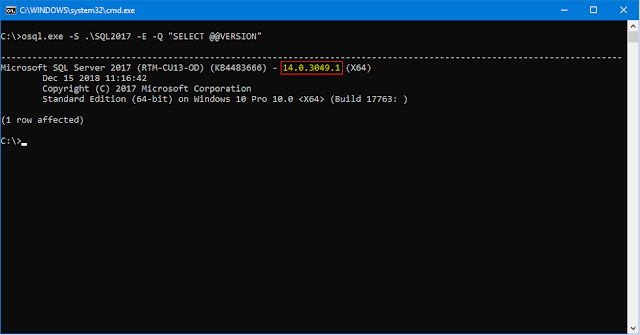
Method 6: OSQL Utility
OSQL is a part of the SQL Server Client Tools (obsolete but still functional).
osql.exe -S ServerName\InstanceName -E -Q "SELECT @@VERSION"
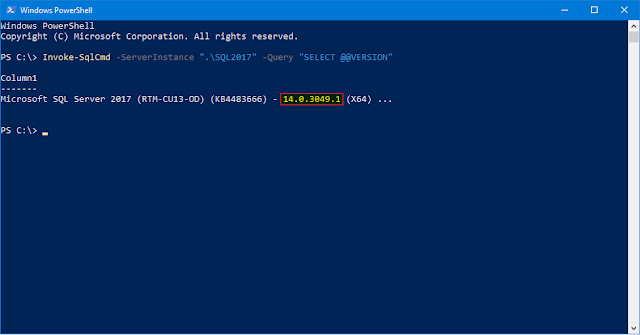
Method 7: Windows PowerShell
Example:
# The SQLPS module must be installed
Import-Module SQLPS
Invoke-SqlCmd -ServerInstance ".\SQL2017" -Query "SELECT @@VERSION"
Command line examples
Example 1: A batch that creates a CSV file with versions from multiple SQL Servers
Windows batch SqlServerVersionsToCsv.cmd:
echo SQLServer,Version > SQLServerVersions.csv set query="SET NOCOUNT ON; SELECT CONCAT(CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(30)), ',', CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ProductVersion') AS VARCHAR(30)));" sqlcmd.exe -S Server1\Instance1 -E -h-1 -W -Q %query% >> SQLServerVersions.csv sqlcmd.exe -S Server1\Instance2 -E -h-1 -W -Q %query% >> SQLServerVersions.csv sqlcmd.exe -S Server2\Instance1 -E -h-1 -W -Q %query% >> SQLServerVersions.csv . . etc.
You need to replace the ServerX\InstanceY with your SQL Server names, e.g. (local)\SQL2017, (local)\SQL2016.
Typical result – content of the file SQLServerVersions.csv:
SQLServer,Version SERVER1\SQL2017,14.0.3049.1 SERVER1\SQL2016,13.0.5239.0 SERVER2\SQL2014,12.0.6205.1
You can comment here.
I work on this site continuously and keep the information up to date. If it helps you, you can support me:


Other useful links:
© 2007–2025 SqlServerVersions.com · Contact · Disclaimer · Privacy policy